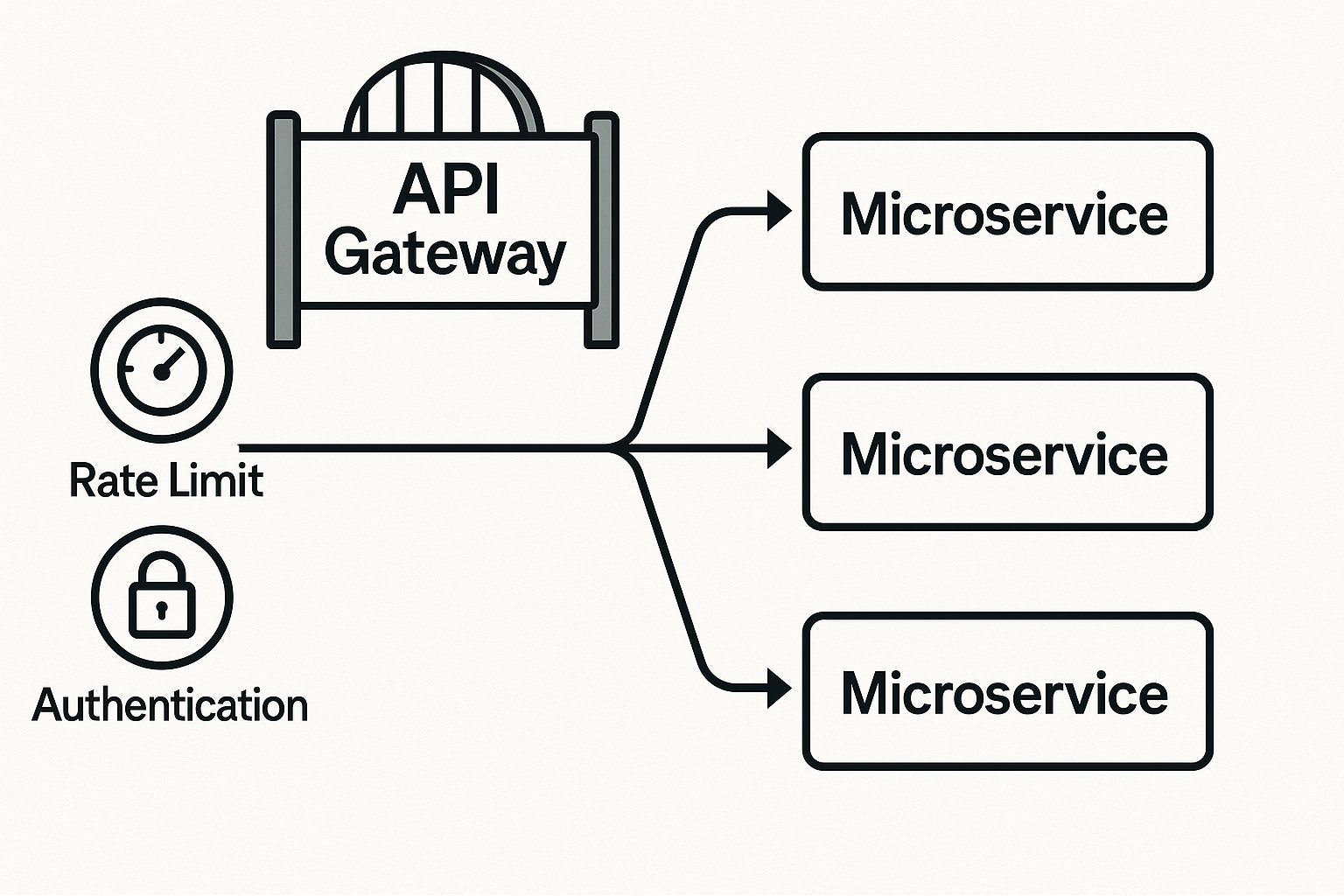
CI/CD fundamentals: why automate deployment
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) streamlines development by automatically testing, building, and deploying code changes. Instead of manually uploading files via FTP or running scripts, developers push to GitHub and let workflows handle the rest.
Benefits for WordPress and static sites:
- Consistency: Every deployment follows the same tested process.
- Speed: Updates move from commit → production within minutes.
- Safety: Automated tests catch issues before going live.
- Rollback readiness: Version control + automated deploys make reverting painless.
GitHub Actions basics for non-DevOps developers
GitHub Actions is GitHub’s native CI/CD service. It runs workflows defined in YAML files inside .github/workflows/.
Workflow syntax and key concepts
name: Deploy Website
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Run build
run: npm run build
Key elements:
on→ triggers (push, pull_request, schedule).jobs→ groups of steps.steps→ tasks using actions or shell commands.
Runners, secrets, and environment setup
- Runners: Virtual machines that execute workflows (
ubuntu-latest,windows-latest). - Secrets: Encrypted variables (API keys, DB credentials) stored in repo settings.
- Environments: Define rules for staging vs production (manual approvals, secrets scoping).
Complete WordPress CI/CD pipeline
WordPress adds complexity because it’s not just code—it’s also plugins, themes, and databases.
Automated testing: unit, integration, security
- PHPUnit for custom plugin/theme code.
- Integration tests using WP-CLI.
- Security scans with tools like PHPStan or
wpscan.
Staging deployment and database sync challenges
- Push code to a staging server via SSH or GitHub Action deployer.
- Use plugins/tools for database sync: WP Migrate DB Pro, WP-CLI export/import.
- Best practice: keep content edits in production, push code from GitHub.
Production deployment strategies (blue-green, rolling)
- Blue-Green: Two environments; switch DNS to the new one after deploy.
- Rolling: Deploy gradually across servers/CDN nodes.
- Basic WordPress deploy: Sync theme/plugin files via SSH/rsync + run
wp core update-db.
Example Action for WordPress via rsync:
name: Deploy WordPress Theme
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Sync theme files
run: rsync -avz --delete ./wp-content/themes/mytheme/ user@server:/var/www/html/wp-content/themes/mytheme/
env:
SSH_KEY: ${{ secrets.SSH_PRIVATE_KEY }}
Static site CI/CD: Jekyll, Hugo, Next.js
Static sites are easier—no database, only files.
Build optimization and caching strategies
- Cache dependencies (
npm ci+actions/cache). - Minify assets before deploy.
- Use GitHub Pages or Netlify for instant builds.
- name: Cache Node modules
uses: actions/cache@v4
with:
path: ~/.npm
key: ${{ runner.os }}-node-${{ hashFiles('**/package-lock.json') }}
CDN invalidation and DNS propagation
- Use Cloudflare Pages or AWS S3 + CloudFront.
- After deploy, run cache purge:
- name: Purge Cloudflare Cache
uses: jakejarvis/cloudflare-purge-action@v0.3.0
with:
apiToken: ${{ secrets.CF_API_TOKEN }}
zone: ${{ secrets.CF_ZONE_ID }}
Security best practices in CI/CD workflows
- Store credentials in GitHub Secrets only.
- Use deploy keys with least privilege.
- Add branch protection rules (require PR reviews before deploy).
- Run security scans automatically (
npm audit,composer audit).
Monitoring and rollback strategies
- Integrate monitoring tools: UptimeRobot, Datadog, Sentry.
- For WordPress, keep database backups before deployment.
- For static sites, rollback = redeploy a previous commit.
Cost optimization: runner usage and workflow efficiency
- Combine multiple steps in one job to save boot time.
- Use matrix builds only when needed.
- Schedule nightly builds instead of building on every commit if deploy frequency is low.
Troubleshooting common issues and debugging techniques
- Workflow stuck → check syntax with
act(local runner). - Secrets not found → verify environment scoping.
- Deployment fails → add
set -xto shell steps for verbose logging. - Rsync/SSH errors → confirm key formatting (
-----BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----).
CI/CD with GitHub Actions empowers WordPress and static site developers to ship faster and safer. WordPress requires extra care with database/content sync, while static sites benefit from simpler pipelines and CDN-powered performance. The key is starting small (basic deploy workflows), then layering on testing, staging, monitoring, and rollback strategies as your project grows.
FAQs
Can I use GitHub Actions for shared hosting WordPress?
Yes, if the host supports SSH or FTP. Otherwise, consider GitHub → deployment via cPanel hooks.
Do I need Docker for WordPress CI/CD?
Not required, but containers simplify testing environments.
Is GitHub Actions free?
Free for public repos; private repos get 2,000–3,000 free minutes/month. Beyond that, billed per minute.